When learning a new language, this connection becomes even more apparent, as our emotions can significantly impact our ability to acquire and retain new linguistic skills.
Emotions are not just by-products of the learning process; they are a part of it. They can either propel us forward with enthusiasm or hold us back with fear and anxiety.
In this blog post, we'll explore how emotions affect language learning and how they shape our experiences by providing insights into how we can use them to enhance our language-learning journey.

The Connection Between Language and Emotion
Language and emotion are deeply intertwined in our everyday communication. Emotions give words their power and meaning, influencing how we convey and interpret messages. When we speak, our choice of words, tone, and body language are all colored by our emotions, making communication a complex dance of verbal and non-verbal cues.
For instance, a simple phrase like "I'm fine" can convey a myriad of emotional states depending on the speaker's intonation and facial expression. In turn, the language we use can evoke specific emotions in ourselves and others, shaping our interactions and relationships.
Linguistic Relativity
The connection between language and emotion extends into the realm of linguistic relativity, a concept explored by the Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis. This theory suggests that the language we speak influences our perception of reality, including our emotional experiences. According to this hypothesis, different languages encapsulate different ways of thinking and feeling.
For example, some languages have multiple words for emotions that are more nuanced than those in other languages, allowing speakers to express and experience their feelings in distinct ways. This suggests that learning a new language can expand our emotional repertoire, offering new ways to understand and articulate our inner lives.
How Do Emotions Affect Learning?
Emotions play a significant role in cognitive processes, including attention, memory, and learning. Positive emotions, such as excitement and curiosity, can enhance attention and motivation, making it easier to focus on and absorb new information. When we are emotionally engaged, our brain releases neurotransmitters like dopamine, which facilitate the encoding and retrieval of memories.
On the other hand, negative emotions can disrupt cognitive functions. Stress and anxiety, for example, can impair our ability to concentrate and remember information, creating barriers to effective learning. Thus, understanding and managing emotions is crucial for optimizing the language learning process.
Read Also:

Positive Emotions and Language Acquisition
Motivation and Enjoyment
Positive emotions like excitement and curiosity are powerful drivers of motivation, which is essential for successful language learning. When learners are genuinely interested and engaged, they are more likely to invest time and effort into practicing and studying.
Excitement about discovering new cultures, understanding different perspectives, and connecting with others through a new language can transform the learning process into an enjoyable and rewarding experience. Curiosity encourages learners to explore beyond the basics, delve into idiomatic expressions, and understand the nuances of the language, leading to a deeper and more comprehensive grasp of the material.
Building Confidence
Confidence is a critical component in the practice and use of a new language. When learners feel confident, they are more willing to take risks, make mistakes, and learn from them. Confidence helps to overcome the fear of judgment or embarrassment, which can be significant barriers to language acquisition.
Learners can develop a more resilient and proactive approach to language learning by gradually building confidence through small successes and positive reinforcement. Engaging in regular practice, celebrating progress, and receiving constructive feedback are essential strategies for boosting confidence and facilitating continuous improvement.
Social Interaction
Positive social experiences play a vital role in language learning and retention. Interacting with native speakers, participating in language exchange programs, and engaging in social activities provide practical opportunities to use the language in real-life contexts. These interactions not only reinforce vocabulary and grammatical structures but also enhance cultural understanding and empathy.
Social interactions make language learning more dynamic and contextually rich, fostering a sense of community and belonging. Moreover, positive feedback and encouragement from peers and instructors can significantly boost motivation and confidence, creating a supportive environment that nurtures ongoing learning and development.
Negative Emotions and Barriers to Language Learning
Common Barriers
Negative emotions can significantly impede language learning, with common barriers including:
Fear of Embarrassment: Many learners are afraid of making mistakes and being judged by others, which can lead to reluctance in speaking or participating in conversations.
Frustration: Language learning can be challenging, and repeated difficulties or slow progress can cause frustration, and diminish motivation and enjoyment.
Lack of Motivation: Without clear goals or intrinsic interest, learners may struggle to maintain the effort and consistency needed for effective language acquisition.
Anxiety And Language Learning
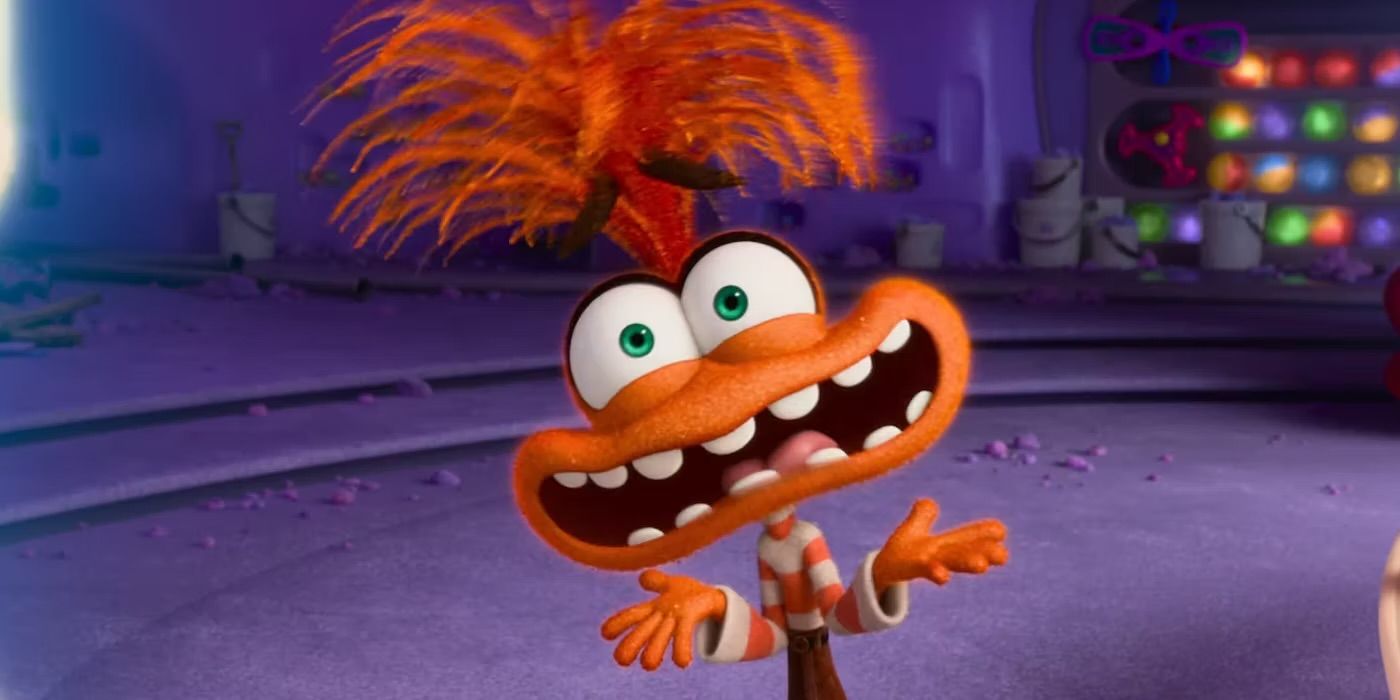

Anxiety is one of the most common emotional barriers to language learning. In the movie Inside Out 2, the character Fear vividly illustrates how anxiety can suppress personality and inhibit one's willingness to take risks, such as speaking in a new language. Fear of making mistakes often leads to a reluctance to practice speaking, which is essential for language acquisition.
Psychologically, anxiety can lead to negative self-talk, reduced self-esteem, and a heightened fear of judgment from others. These effects can create a vicious cycle where anxiety hampers language practice, leading to slower progress and increased frustration.
How To Manage Negative Emotions?
To overcome these barriers and manage negative emotions, consider the following strategies:
- Embrace Mistakes as Learning Opportunities: Shift the perspective on mistakes, viewing them as a natural part of the learning process. Remind yourself that every error is a step towards improvement and greater proficiency.
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable, short-term goals to create a sense of accomplishment and maintain motivation. Break down larger tasks into manageable steps to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Treat yourself with kindness and understanding when you encounter difficulties. Acknowledge the effort you are putting into learning and avoid harsh self-criticism.
- Engage in Relaxation Techniques: Use mindfulness, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to reduce stress and anxiety. These practices can help create a calm and focused mindset conducive to learning.
- Seek Positive Social Support: Surround yourself with supportive peers, instructors, or language exchange partners who can provide encouragement and constructive feedback. Positive social interactions can boost confidence and motivation.
- Create a Positive Learning Environment: Designate a comfortable and distraction-free study space. Use resources that match your learning style and keep the learning process enjoyable with varied activities like games, music, or cultural exploration.
- Celebrate Progress: Regularly reflect on and celebrate your achievements, no matter how small. Recognizing your progress can help maintain motivation and a positive attitude toward learning.
Read Also:

Emotional Intelligence in Language Learning
Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is a fundamental aspect of emotional intelligence that plays a crucial role in language learning. It involves recognizing and understanding your own emotions, which can help you manage them effectively. By being aware of how you feel during different stages of the learning process, you can identify what triggers negative emotions such as frustration or anxiety, and take proactive steps to address them.
For example, if you notice that speaking in front of others makes you anxious, you can practice relaxation techniques beforehand or seek out supportive speaking environments. Self-awareness also helps in recognizing moments of joy and satisfaction, allowing you to build on these positive experiences and maintain motivation. By tuning into your emotional responses, you can create a more tailored and effective learning strategy.
Empathy and Communication
Empathy, another key component of emotional intelligence, involves understanding and sharing the feelings of others. In the context of language learning, empathy can significantly enhance your communication skills and cultural competence. By putting yourself in the shoes of native speakers or fellow learners, you can better grasp the subtleties of their language and cultural expressions. Empathy allows you to pick up on non-verbal cues, such as tone of voice and body language, which are essential for effective communication.
Moreover, empathy fosters patience and open-mindedness, enabling you to navigate cross-cultural interactions more smoothly. When you understand the emotions and perspectives of others, you can respond more appropriately and build stronger, more meaningful connections. This not only improves your language skills but also enriches your overall learning experience by providing deeper insights into the cultural context of the language you are learning.
Tips For Using Emotions In Language Learning
Creating a Positive Learning Environment
Creating an emotionally supportive learning environment is crucial for maximizing language learning success. Here are some tips to achieve this:
- Personalize Your Space: Designate a comfortable, distraction-free study area. Surround yourself with materials and decorations that inspire and motivate you.
- Incorporate Variety: Use diverse learning resources such as books, apps, podcasts, and videos to keep the process engaging and prevent monotony.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward yourself for milestones achieved, no matter how small. Celebrating successes boosts motivation and reinforces positive emotions.
- Supportive Community: Engage with supportive peers, language partners, or study groups. A positive social network provides encouragement, feedback, and a sense of camaraderie.
- Encouraging Atmosphere: Choose environments, whether online or in-person, that foster a welcoming and non-judgmental atmosphere where making mistakes is seen as a natural part of learning.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting achievable goals is essential for maintaining motivation and fostering positive emotions. Here's how to set effective goals:
- Specific and Measurable: Define clear, specific goals that can be measured. For example, aim to learn 10 new vocabulary words a week or have a 5-minute conversation in the target language daily.
- Break Down Larger Goals: Divide larger goals into smaller, manageable steps. This approach helps to avoid feeling overwhelmed and ensures steady progress.
- Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Balance short-term goals, which provide immediate satisfaction, with long-term goals that guide your overall learning journey.
- Flexible and Adaptable: Be open to adjusting your goals as you progress. Flexibility allows you to adapt to new challenges and maintain a positive attitude.
- Track Progress: Keep a journal or use apps to monitor your achievements. Seeing tangible progress can boost motivation and reinforce your commitment to learning.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Managing stress and anxiety through mindfulness and relaxation techniques can enhance your learning experience. Here are some effective practices:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practice mindfulness meditation to stay present and focused. Techniques such as deep breathing, body scans, and guided meditations can reduce stress and increase concentration.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Use progressive muscle relaxation exercises to relieve physical tension. This technique involves tensing and then slowly releasing different muscle groups to promote relaxation.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Engage in deep breathing exercises to calm the mind and body. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing or the 4-7-8 method can be particularly effective.
- Visualization: Visualize yourself successfully using the language in various scenarios. Positive visualization can reduce anxiety and build confidence.
- Regular Breaks and Physical Activity: Incorporate regular breaks and physical activities into your study routine. Physical exercise can reduce stress hormones and increase endorphins, improving mood and cognitive function.
Final Words
In learning a new language, emotions play a vital role, influencing everything from our motivation to our ability to connect with others. Throughout this discussion, we've seen how our feelings can either propel us forward or hold us back!
Learn New Languages By Watching Movies With Lingopie!
Who says learning can’t be fun? Grab some popcorn and immerse yourself in foreign films or binge-watch TV shows. That's the mission of Lingopie, making language learning fun and immersive!
Lingopie makes learning a new language fun and effective by using real TV shows, movies, and documentaries. It offers interactive subtitles, so you can click on any word to get an instant translation and pronunciation. If this sounds fun to you, download Lingopie from the App Store or Play Store now and get a FREE 7-day trial!







![Language Difficulty Ranking For English Speakers [2025]](/blog/content/images/size/w300/2025/05/Language-Difficulty-Ranking----For-English-Speakers.png)
![Language Learning with Netflix [2025 Guide]](/blog/content/images/size/w300/2023/05/Netflix-AD.jpg)

