Most people assume they'll get by with English in Japan, but here's the reality: fewer than 30% of Japanese people speak English at any level. With less than 8% speaking it fluently, knowing how to say thank you in Japanese or ask where the bathroom is can literally make or break your trip.
In this post, we'll cover 50+ essential Japanese phrases that'll help you navigate restaurants, train stations, and shops while showing respect for Japanese culture. Plus, we'll share pronunciation tips to make you sound more natural and actually learn Japanese the right way!
- How To Say Good Luck In Japanese [12+ Easy Ways]
- 10 Best Movies & Shows to Learn Japanese on Netflix
- The Cheat Code to Learn Japanese With Movies
Can You Survive in Japan Without Speaking Japanese?
Technically, yes but your experience will be significantly limited. Recent data shows that only 15-28% of Japanese people speak English at any conversational level, with less than 2% speaking it fluently. Tokyo scores highest for English proficiency with 496 out of 800 points, but even that's considered "low proficiency" on international scales.
Here's what you can realistically expect:
- Major tourist areas (Tokyo, Kyoto, Osaka) have bilingual signs and some English-speaking staff
- Hotels and popular restaurants often have English menus and basic English speakers
- Train stations in big cities display English alongside Japanese
- Google Translate with camera function works well for signs and menus
- Rural areas and local establishments have virtually no English support
- Emergency situations become genuinely challenging without Japanese phrases
Your survival depends heavily on where you go and what you need. Shopping for souvenirs in Shibuya? You'll manage. Dealing with a medical emergency in rural Kyushu? You'll desperately wish you knew basic Japanese. Even in Tokyo, many locals who know some English are often too nervous to use it because they're afraid of making mistakes and potentially embarrassing themselves.
10 Essential Japanese Words And Phrases
When starting to learn Japanese, it's helpful to familiarize yourself with some essential words and phrases. These basic expressions can help you navigate common social situations, communicate politely, and express yourself in simple ways.
From greetings and gratitude to requests and acknowledgments, the following Japanese phrases are fundamental building blocks for beginner learners. Let's explore their meanings and contexts:
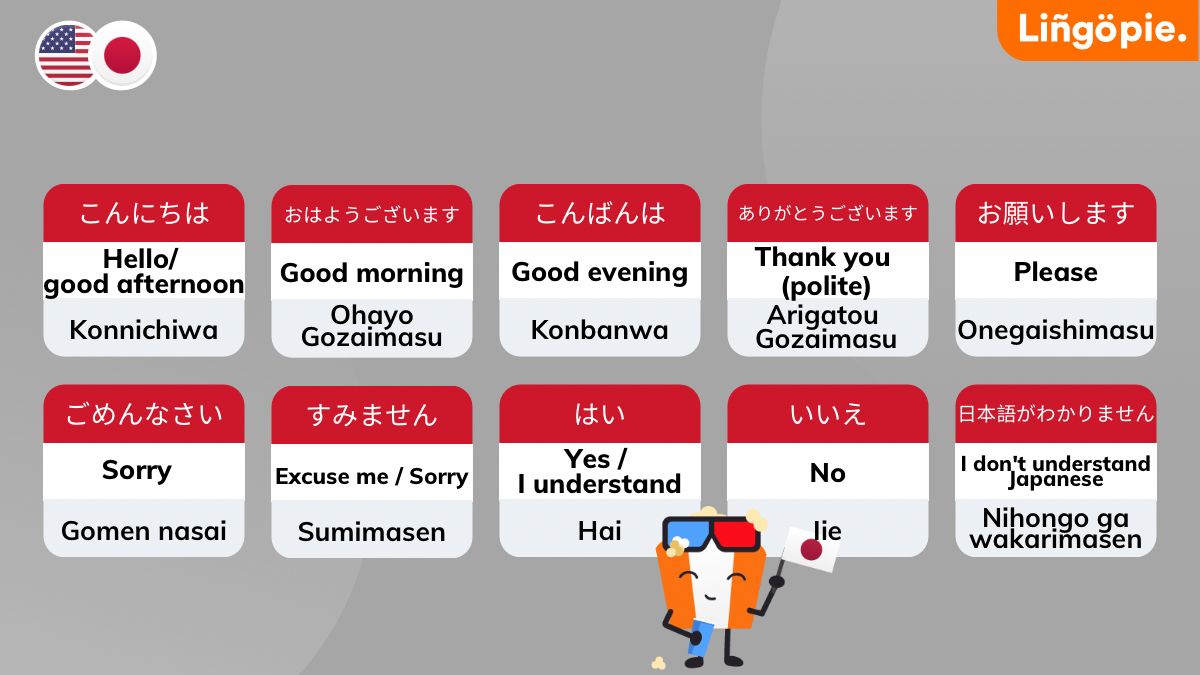
- Konnichiwa (こんにちは) – Hello/Good afternoon
A basic greeting used during the day. Suitable for use with strangers or casual acquaintances. - Ohayou Gozaimasu (おはようございます) – Good morning
A polite way to greet someone in the morning. Useful for formal situations or when addressing elders/superiors.
Note: The "u" in "Ohayou" is often silent, so it sounds like "Ohayo." - Konbanwa (こんばんは) – Good evening
The evening greeting counterpart to "Konnichiwa." Appropriate for use from around sunset onwards. - Arigatou Gozaimasu (ありがとうございます) – Thank you (polite)
"Arigatou" is the basic way to express thanks. Adding "Gozaimasu" makes it more formal. Note: The "u" in "Arigatou" is often silent, so it sounds like "Onegaishimasu (お願いします) / Kudasai (ください) – Please
"Onegaishimasu" is more formal, while "Kudasai" is slightly more casual. Both express requests politely. - Sumimasen (すみません) – Excuse me/Sorry
A versatile phrase used to apologize, get attention politely, or ask for a favor humbly. - Hai (はい) – Yes/I understand
The most basic way to express agreement or acknowledge something. - Iie (いいえ) – No
A simple, polite way to express negation or disagreement. - Nihongo ga wakarimasen (日本語がわかりません) – I don’t understand Japanese
Useful for communicating language limitations politely when first learning Japanese. - Gomen nasai (ごめんなさい) – I’m sorry
An important phrase to apologize sincerely in both formal and informal contexts.
How to Show Formality in Japanese
Before we continue with our list of Japanese phrases, let's talk about Japanese formality first. In Japan, social hierarchy determines how you speak to someone, with a generally accepted order: customers above shopkeepers, elders above younger people, bosses above employees. As a tourist, you'll almost always be in situations where formal language is expected.
To avoid sounding rude, here are some details you need to know.
Making "Thank You" Polite
The word "arigatou" becomes much more respectful when you add "gozaimasu" to the end. Here's how it works:
- Arigatou gozaimasu (ありがとうございます) is your go-to formal "thank you" for service staff, strangers, and anyone you want to show respect to.
- Domo arigatou gozaimasu (どうもありがとうございます) is even more polite—think "thank you very much."
For casual situations with friends or family, just arigatou (ありがとう) or domo (どうも) works fine, but as a tourist, you'll rarely need these informal versions.
The Two Ways to Say "Please"
Japanese has two main words for "please," and choosing the right one shows your understanding of the situation.
- Onegaishimasu (お願いします) is the more formal, humble option. Use this when making requests of service staff or anyone you want to show extra respect to. "Mizu onegaishimasu" (水をお願いします) means "Water, please" in a very polite way.
- Kudasai (ください) is more direct and familiar. You'd use this with friends, peers, or when you feel entitled to something. "Mizu kudasai" (水をください) is more like "Give me water, please."
When in doubt as a tourist, onegaishimasu is always the safer choice. It shows humility and respect, which Japanese culture values highly.
When Formality Really Matters
Getting formality wrong can create awkward situations, but getting it right opens doors. If you're asking someone to repeat something because you didn't understand, "Mou ichido onegaishimasu" (もう一度お願いします) shows respect for their time and effort.
Oh, and don't forget about your body language. A slight bow (about 15 degrees) when saying thank you or making a request shows you understand Japanese customs. You don't need to master the deeper 30 or 45-degree bows but knowing at least how to do a small nod of respect goes a long way.

10 Food & Drink Basic Phrases in Japanese
| Japanese | Romaji | English | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| メニュー | Menyū | Menu | メニューをください (Menyū o kudasai) – "The menu, please." |
| お酒 | O-sake | General term for alcohol | お酒が好きです (O-sake ga suki desu) – "I like alcohol." |
| 日本酒 | Nihonshu | Japanese saké (rice wine) | 日本酒をください (Nihonshu o kudasai) – "Saké, please." |
| ビール | Bīru | Beer | ビールを一杯ください (Bīru o ippai kudasai) – "One beer, please." |
| 水 | Mizu | Water | 水をください (Mizu o kudasai) – "Water, please." |
| ご飯 | Gohan | Rice | ご飯をください (Gohan o kudasai) – "Rice, please." |
| みそ汁 | Misoshiru | Miso Soup | みそ汁をください (Misoshiru o kudasai) – "Miso soup, please." |
| すし | Sushi | Sushi | すしをください (Sushi o kudasai) – "Sushi, please." |
| 餅 | Mochi | Mochi (a traditional Japanese glutinous rice cake) | 餅をください (Mochi o kudasai) – "Mochi, please." |
| ___をください | ___ o Kudasai | I would like __, please | 水をください (Mizu o kudasai) – "Water, please." |
| ___をお願いします | ___ o Onegaishimasu | I would like __, please (more formal) | 水をお願いします (Mizu o onegaishimasu) – "Water, please." (polite) |
In addition to food and drink, you might want to know how to ask for other specific services in a Japanese restaurant.
- Kin'en seki (禁煙席) - Non-smoking seat
- Kurejittokādo wa tsukaemasu ka? (クレジットカードは使えますか) - Do you accept credit cards?
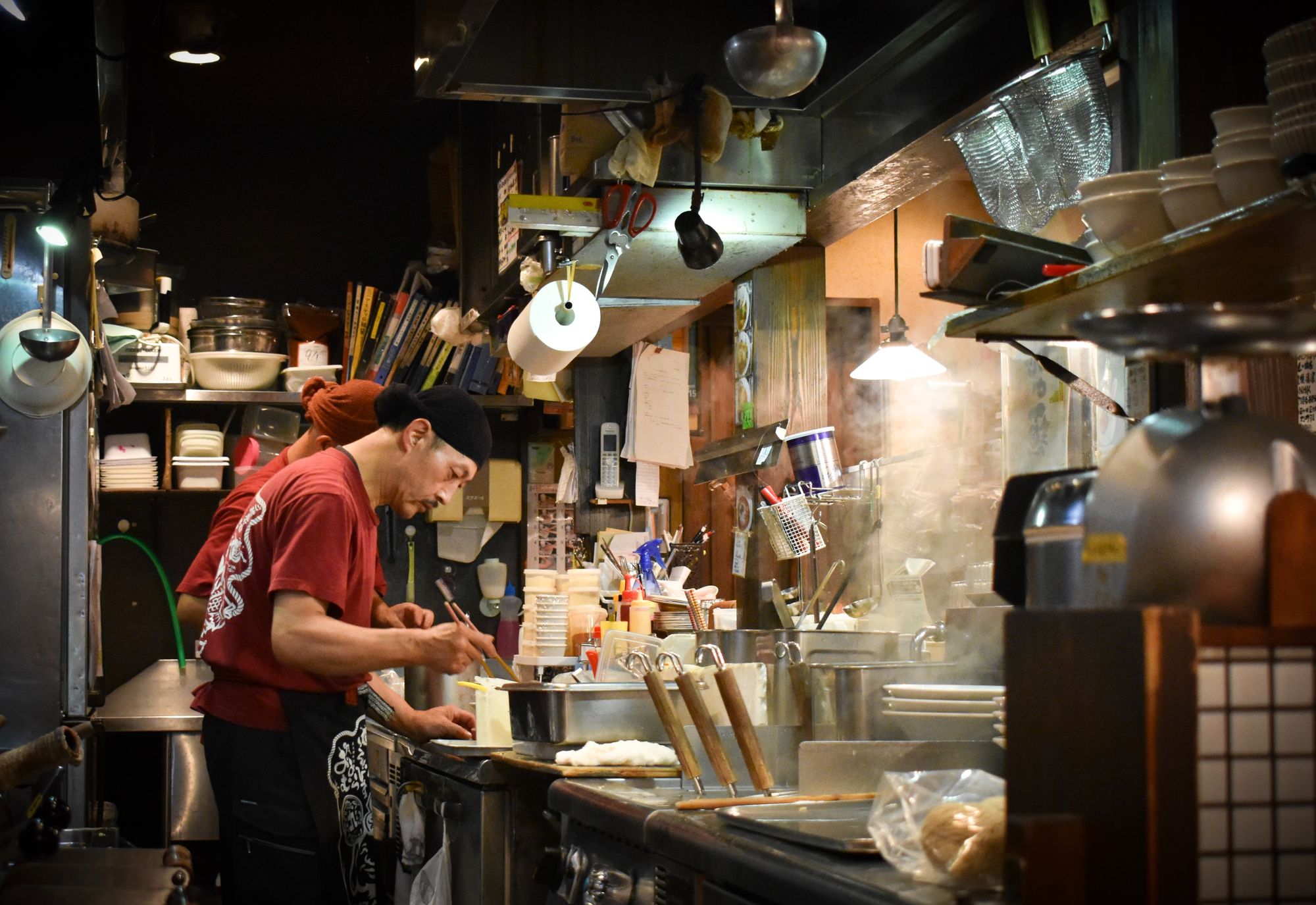

Japanese Restaurant Etiquette
It is not enough simply to know a few polite phrases in Japanese. You will also need to understand a bit about restaurant etiquette.In many Japanese restaurants, there are low tables with cushions, rather than or in addition to western-style tables and chairs.
Cushions will be placed on tatami floors, which are a traditional kind of mat flooring in Japanese restaurants. You should never wear shoes or slippers on tatami flooring, and avoid stepping on anyone's cushion except your own.
Japanese Restaurant Vocabulary in Context
When the food comes, it is customary to wait for everyone's meals to arrive, then say:
Itadakimasu (いただきます) - "I gratefully receive (this meal)"
You should say this before starting to eat. This is similar to the French "bon appetit". This phrase is used to express gratitude for the meal, similar to saying grace.
However, if a dish is best eaten hot and it arrives before the others, the following phrase can be used:
- Osaki ni douzo (お先にどうぞ) - "Please go ahead"
Other useful Japanese resturant phrases include:
- Daijoubu Desu (だいじょうぶです) - "I'm fine now" (this is a polite way to decline something from a waiter offering you more water or food).
You can conclude the meal by saying the phrase:
- Gochisousama deshita (ごちそうさまでした) - "Thank you for the feast."
This expresses gratitude to the chef and for the ingredients of the meal.
At the end of your meal, you should use the following:
- Okaikei wo onegaishimasu (お会計をお願いします) - "The check, please."
Manners in Convenience Stores
The following piece of vocabulary will be useful:
Konbini (コンビニ) - Convenience store
In Japan, simple things like unfolding your bills before you hand them over to the cashier and not throwing down your coins are considered polite as they make the worker's job easier. Customer service in Japan is famously excellent, so treat the clerk with respect and kindness, as you should in any other foreign country.
10 Transportation-Related Phrases In Japanese
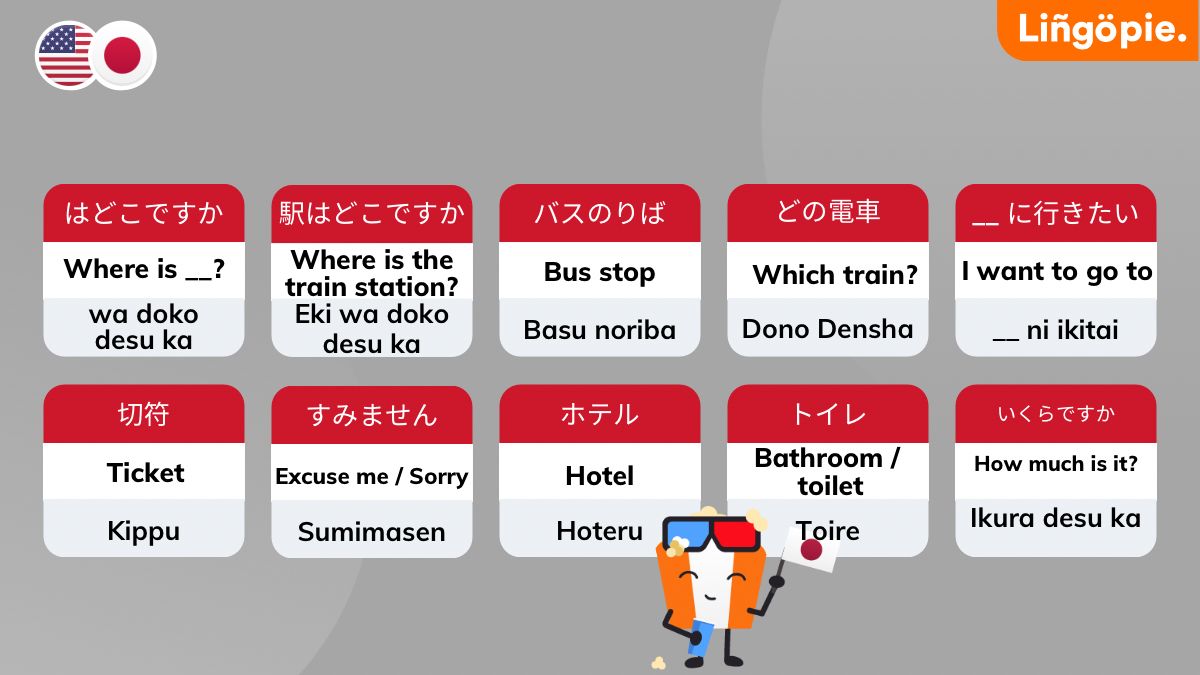
- ___wa doko desu ka (はどこですか) – Where is __?
- Eki (駅) - Train station
eg. Eki wa doko desu ka (駅はどこですか) - Where is the train station? - Basu noriba (バスのりば) - Bus stop. It’s worth noting that "noriba" (乗り場) means "boarding place" or "stop."
- Dono Densha (どの電車)/ Dono basu (どのバス) – Which train?/ Which bus?
- (Tōkyō) ni ikitai ([東京) に行きたい) – I want to go to (Tokyo)
- Kippu (切符) – Ticket
- Katamichi kippu (片道切符)/ Kaeri no kippu (帰りの切符) - One-way ticket/ return ticket
- Hoteru (ホテル) - hotel
- Toire ( = トイレ) - Bathroom / toilet
- Ikura desu ka (いくらですか) - How much is it?
Japanese travel phrases in context
Now, you can start to put some of the words we have learned together to create a proper phrase.
- Hiroshima e no kaeri no kippu o onegai shimasu, ikura desu ka (広島への帰りの切符をお願いします、いくらですか) - "I would like a return ticket to Hiroshima, how much is it?"
These essential Japanese travel phrases will come in handy when visiting Japan, as an estimated 70% of the population does not speak English. You'll find more people with some level of English in the top destinations, such as Tokyo, Kyoto, and Osaka, while you might hit a language barrier in smaller towns.
10 Time-Related Phrases In Japanese
Whether you're inquiring about the current time, referring to specific times of the day, or discussing dates, these Japanese time phrases will prove invaluable. Let's explore 10 essential time-related words and expressions in Japanese:
| Japanese | Romaji | English | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 今何時ですか | Ima Nanji Desu ka? | What time is it now? | "Nanji" (何時) means "what time." |
| 朝 | Asa | Morning | |
| 今日 | Kyou | Today | |
| 明日 | Ashita | Tomorrow | |
| 何時に? | Nanji ni? | At what time? | |
| 午後 | Gogo | Afternoon | |
| 夜 | Yoru | Night/Evening | |
| 昨日 | Kinou | Yesterday | |
| いつでも | Itsudemo | Anytime/Whenever | |
| 時間がありません | Jikan ga arimasen | I don't have time. | This phrase is formal. A more casual version is 時間がない (Jikan ga nai). |
Basic Japanese Phrases and Pronunciation
An important phrase you will likely say a lot is desu ka (ですか). This indicates a question when placed at the end of a sentence. So, let's make sure you can say it correctly, as it may not be pronounced as you'd expect. You want to pronounce desu like “dess.” Remember, the “u” sound at the end is dropped. This happens a lot with words that end with “u” sounds, including:
- Arigatou Gozaimasu (ありがとうございます) - "thank you" (which is pronounced "arigatou gozaimas").
We have already seen desu ka in the phrase ikura desu ka, "how much is it?", and wa doko desu ka, "where is it?".
It is also used in the following key Japanese phrases:
- O genki desu ka (お元気 です 化) - How are you?
(Pronounced "o genki dess ka"). - Nani desu ka (何ですか なにですか) - (polite) What?
- Sou desu ka (そうですか) - Is that so?/ Really?
The response, Sou desu (そうです), pronounced "so dess", means "that is so" or "yes, really". - Kore wa na ndesu ka (これ わ なん です か) - What is this?
You can create many more Japanese phrases for asking questions by using desu ka, so try to remember this pronunciation as it will get you a long way.
Basic Greetings Tourists Should Know in Japan
If you only have a short time before your trip to Japan, at the very least learn these simple greetings and make sure you know the dos and don'ts of public affection.
- Kon'nichiwa, watashinonamaeha ___ (こんにちは、私の名前は) - "Good afternoon, my name is ___"
- Konbanwa, hajimemashite (こんばんは、はじめまして) - "Good evening, nice to meet you."
- Namae wa nandesu ka? (名前はなん です か) - "What is your name?"
Making Friends in Japan
Now that you know how to greet Japanese people appropriately, you can start to build a relationship with them.
Generally, when you meet people while traveling abroad, you ask:
- Eigo o hanashimasu ka? (英語を話せますか) - "Can you speak English?"
- Anata wa doko no kuni no shusshindesu ka (あなたはどこの国の出身 です か) - "Which country are you from?"
- Doko no shusshindesu ka? (どこの出身 です か) - "Where are you from?" (more simple phrase).
- Anata wa doko ni sun deru nodesu ka? (あなたはどこに住んでるの です か) - "Where do you live?"
If you would like to become friends or make a date, you might want to gauge the person's interests:
- Anata wa (eiga ga) sukidesuka? (あなたは (映画が) 好き です か) - "Do you like (the cinema)?"
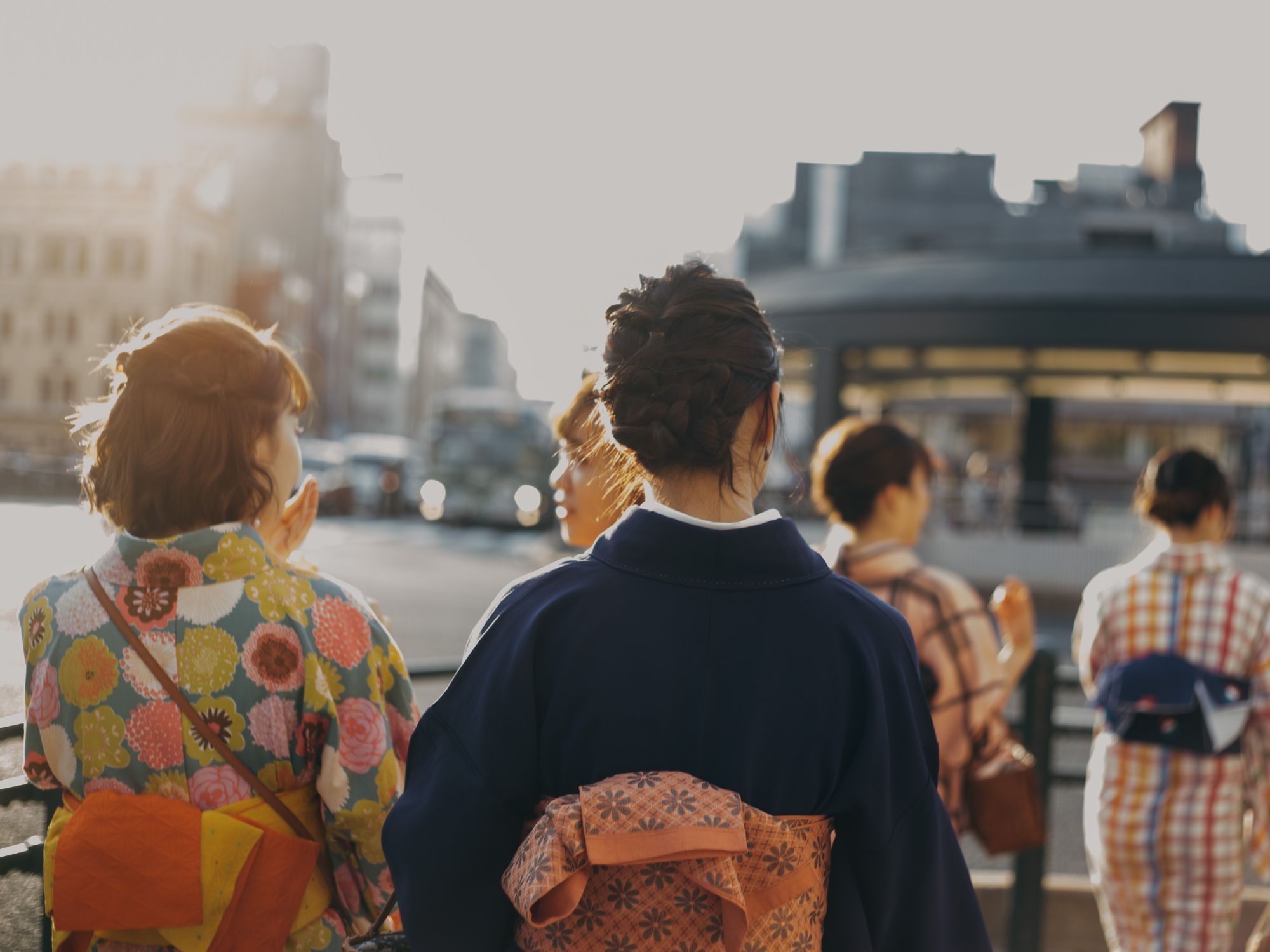

Travel Tips for Japan
Remember Japanese manners! This includes restaurant etiquette, limiting public displays of affection, using polite language, and respecting the culture. You cannot expect everyone in the world to speak your language, but by using a simple Japanese phrase here and there you can show that you are willing to try and meet them halfway.
Choose the season wisely. Visit Japan in Winter for the ski season, or in Spring for unforgettable views of cherry blossoms. Or, choose an Autumn trip to avoid tourist crowds and peak travel seasons. The same applies to Summer, though this is typhoon season, which puts a lot of tourists off.
What is Ryokou?
Ryokou (旅行) is a Japanese noun meaning "travel" or "trip", while "Tabi" (旅) refers to a journey or pilgrimage. Broken down, 旅 is the kanji character meaning "travel", "trip", or "journey", and 行 is the kanji character used to express the act of going or visiting. Use this next phrase if you want to impress your new Japanese friends by using their local language:
- Watashi wa ryokou ga sukidesu (私は旅行が好きです) - "I love traveling".
If you're studying Japanese so you can take a trip to Japan, this is undoubtedly true!
How to Learn Japanese Naturally
If you are looking for additional resources for learning Japanese, check out Lingopie.
This is an online streaming platform that is designed to get you speaking Japanese and learning Kanji with ease through immersion in Japanese TV and movies. Lingopie provides an authentic and natural way to learn other languages and makes learning Japanese fun. This is a great tool for busy people who cannot sit through hours of Japanese classes every week.
Simply relax in the evening and watch half an hour of Japanese TV. Allow your brain to absorb the language naturally and pick up useful phrases and pronunciation. And if you want to keep binge watching awesome shows check out our other Japanese articles. We listed 9 Japanese Movies on Netflix that can help your studies and we also did a guide to learning Japanese with anime! We also recommend you to check out our free guide "Best way to learn Japanese".
Ready To Speak Japanese?
These 50+ phrases will get you through your Japan trip, but what if you could actually understand what people are saying back to you? Imagine watching a Japanese drama and catching jokes, cultural references, and subtle emotional nuances that no phrasebook could ever teach you.
With Lingopie, you're not drilling vocabulary lists. Instead, you're binge-watching authentic Japanese content while subtly absorbing the language. Curious how much Japanese you could pick up from just one episode of your favorite show? There's only one way to find out.
FAQs About Japanese Phrases for Tourists
What are some helpful tourist phrases in Japan?
Essential Japanese phrases for tourists include:
- Konnichiwa (こんにちは) – Hello/Good afternoon.
- Sumimasen (すみません) – Excuse me/Sorry.
- Arigatou Gozaimasu (ありがとうございます) – Thank you.
- Eki wa doko desu ka? (駅はどこですか) – Where is the train station?
- Toire wa doko desu ka? (トイレはどこですか) – Where is the bathroom?
For more practical phrases, try Lingopie, a platform for learning Japanese through TV shows and movies.
How to speak Japanese for tourists?
Tourists can start with basic greetings like Ohayou Gozaimasu (おはようございます) – Good morning, and polite requests like Onegaishimasu (お願いします) – Please. Questions like Ikura desu ka? (いくらですか) – How much is it? are also useful. Practice with tools like Lingopie to improve pronunciation and fluency.
What do Japanese people say before going out?
Before leaving, Japanese people say Ittekimasu (行ってきます) – "I’m leaving." The response is Itterasshai (行ってらっしゃい) – "Take care." These phrases reflect Japanese politeness and cultural values. Learn more everyday expressions with Lingopie.
Are Japanese polite to tourists?
Yes, Japanese people are known for their politeness and helpfulness toward tourists. They appreciate visitors who try to speak Japanese, even with basic phrases. Politeness is a key part of Japanese culture, so expect friendly greetings and assistance.
What is the slogan of Japan Tourism?
Japan Tourism’s slogan is "Endless Discovery", highlighting the country’s diverse attractions. From Tokyo’s bustling streets to Kyoto’s serene temples, Japan offers something for everyone. Learning a few Japanese phrases can enhance your travel experience.







![How To Use Mo (も) Particle In Japanese Grammar [Guide]](/blog/content/images/size/w300/2025/06/How-To-Use-Mo-----Particle-In-Japanese-Grammar.jpg)


